Lawrence M. Boxt, MD, FACC
- Professor of Clinical Radiology
- Albert Einstein College of Medicine
- Director of Cardiac MRI and CT
- North Shore University Hospital
- Manhasset, New York
Unisom dosages: 25 mg
Unisom packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Buy unisom 25 mg without prescription
Within tracts, interfascicular oligodendrocytes are organized in lengthy rows in which single astrocytes intervene at regular intervals. Groups of oligodendrocytes myelinate the encompassing axons: their processes are radially aligned to the axis of each row. Myelinated tracts subsequently consist of cables of axons, which are predominantly myelinated by a row of oligodendrocytes working down the axis of every cable. Oligodendrocytes originate from the ventricular neuroectoderm and the subependymal layer within the fetus and continue to be generated from the subependymal plate postnatally. Stem cells migrate and seed into white and gray matter to form a pool of grownup progenitor cells that will later differentiate to replenish misplaced oligodendrocytes and possibly remyelinate pathologically demyelinated areas. Oligodendrocytes Blood�Brain Barrier Proteins circulating in the blood enter most tissues of the physique except these of the brain, spinal cord or peripheral nerves. This concept of a blood�brain barrier (and blood�nerve barrier) covers many substances, a few of that are actively transported throughout the blood�brain barrier, whereas others are actively excluded. It is dependent upon the presence of tight junctions between endothelial cells and a relative lack of transcytotic vesicular transport. The tightness of the barrier is decided by the shut apposition of astrocytes to blood capillaries. The blood�brain barrier develops throughout embryonic life however is most likely not totally accomplished by birth. Most of these areas are situated near the ventricles and are often recognized as circumventricular organs. Otherwise, unrestricted diffusion by way of the blood�brain barrier is possible only for substances that may cross biological membranes due to their lipophilic character. Breakdown of the blood�brain barrier happens following mind harm brought on by ischaemia or an infection, and this permits an inflow of fluid, ions, protein and different substances into the mind. It can be associated with major the territory ensheathed by an oligodendrocyte course of defines an internode. The interval between internodes is called a node of Ranvier, and the territory instantly adjoining to the nodal gap is a paranode, where loops of oligodendrocyte cytoplasm abut the axolemma. Nodal axolemma is contacted by the end-feet of perinodal cells, which have been shown in animal research to have a presumptive grownup oligodendrocyte progenitor phenotype; their operate is unknown (Butt and Berry 2000).
Cheap 25mg unisom free shipping
When activated, platelets may kind occlusive thrombi in cardiovascular diseases that lead to myocardial infarction, stroke, or different acute ischemic syndromes of other organs. Increased shear forces and move throughout the endothelium launch important anticoagulation brokers (Table 27-2). This complex equilibrium of hemostasis continues and is constantly scavenged by many of those important mechanisms to localize hemostasis to the site of vascular damage through this multitude of regulatory mechanisms. Coagulation is closely linked to inflammatory responses (hemostatic initiation, contact activation, and other pathways amplify inflammatory responses and can collectively produce end-organ harm within the strategy of their normal perform as host defense mechanisms). Surgical injury and additional activation that may occur following cardiopulmonary bypass produce inflammatory Chapter 27 � Physiology of Blood and Hemostasis 509 responses initiated by contact of blood with the broken vasculature and different nonendothelial extracorporeal circuits. In vascular surgical and trauma patients, ischemia-reperfusion harm of organs also can occur. The two checks most regularly used in the perioperative setting, apart from blood counts, embrace the prothrombin time, used to evaluate the extrinsic coagulation cascade, and the activated partial thromboplastin time, used to consider the intrinsic pathway of the basic coagulation system. Although prothrombin time is used commonly for perioperative coagulation screening, its use and goal values are nonetheless controversial and often primarily based on consensus rather than supportive data. The partial thromboplastin time is one other broadly used coagulation test that assesses the intrinsic coagulation cascade. The partial thromboplastin time is used to monitor lower doses of unfractionated heparin (up to 1. Although these coagulation exams are used to consider bleeding, they solely examine specific components of the general coagulation cascade and may not be helpful to decide the precise explanation for the coagulopathy. Whole blood viscoelastic tests including thromboelastography and thromboelastometry present a number of insights in to coagulation issue interplay and allow assessment of individual traits of either individual limbs of hemostasis or international monitoring of coagulation (widely used in the perioperative and trauma setting). The generally used thromboelastometric variables embrace coagulation time (onset in seconds), clot formation time (initial price of fibrin polymerization in seconds), angle (a; in degrees), 510 Part V � Blood and Hemostasis most clot firmness (in millimeters), and lysis time (in seconds, used for the prognosis of premature lysis or hyperfibrinolysis). In surgical sufferers, there are multiple perioperative events that influence hemostatic operate and produce coagulopathy.
Unisom 25mg mastercard
All pontocerebellar fibres end as mossy fibres in the cerebellar cortex, and a degree of somatotopy is maintained in these connections. The precerebellar pontine nuclei include all the neurones scattered in the ventral pons. They are in all probability all glutamatergic, and most project to the cerebellar cortex, with some enter to the deep cerebellar nuclei. Corticopontine fibres arise primarily from neurones in layer V of the premotor, somatosensory, posterior parietal, extrastriate visible and cingulate neocortices. The terminal fields, although divergent, form topographically segmented patterns resembling overlapping columns, slabs or lamellae within the pons. Subcortical projections to the pontine nuclei embody these from the superior colliculus to the dorsolateral pons, and from the medial mammillary nucleus to the rostromedial pons and pretectal nuclei. The lateral geniculate nucleus, dorsal column nuclei, trigeminal nuclei, hypothalamus and intracerebellar nuclei also project to restricted neurones of the pons. Functionally related subcortical and cerebrocortical afferents converge, for instance, these from the somatosensory cortex, dorsal column nuclei and medial mammillary nucleus. There is also non-specific input from the reticular formation, raphe nuclei, locus coeruleus and paraqueductal gray matter. Each colliculus accommodates the motor nucleus of the abducens nerve and the geniculum of the facial nerve. More deeply positioned are the facial nuclei, the close by vestibular and cochlear nuclei and different isolated neuronal groups. The medial vestibular nucleus continues from the medulla barely into the pontine tegmentum and is separated from the inferior cerebellar peduncle by the lateral vestibular nucleus. The vestibular nuclei are laterally positioned in the rhomboid fossa of the fourth ventricle, subjacent to the vestibular area, which spans the rostral medulla and caudal pons.
Generic unisom 25 mg mastercard
Many subsequently ascend the mind stem within the dorsomedial a part of the medial lemniscus and synapse on probably the most medial neurones of the thalamic nucleus ventralis posterior medialis (in a area sometimes termed the accessory arcuate nucleus). Axons from the nucleus ventralis posterior medialis radiate through the interior capsule to the anteroinferior area of the sensorimotor cortex and the insula. It is assumed that other ascending paths finish in a number of hypothalamic nuclei and thus mediate the route by which gustatory information reaches the limbic system, allowing appropriate autonomic reactions. Swallowing and Gag Reflexes - During the normal processes of consuming and ingesting, passage of fabric to the rear of the mouth stimulates branches of the glossopharyngeal nerve within the oropharynx. This data is relayed through the nucleus solitarius to the nucleus ambiguus, which contains the motor neurones innervating the muscular tissues of the palate, pharynx and larynx. The nasopharynx is closed off from the oropharynx by elevation of the taste bud. Peristaltic activity down the oesophagus to the abdomen is mediated by way of the pharyngeal plexus. There is a reflex contraction of the muscle tissue of the pharynx, soft palate and fauces that, if extreme, could result in retching and vomiting. Nucleus Ambiguus the nucleus ambiguus is a gaggle of large motor neurones located deep within the medullary reticular formation. Caudal fibres join the vagus and cranial accessory nerves and are distributed to the pharyngeal constrictors, intrinsic laryngeal muscles and striated muscles of the palate and higher oesophagus. The nucleus ambiguus incorporates several mobile subgroups, and some topographical representation of the muscle tissue innervated has been established. Individual laryngeal muscular tissues are innervated by relatively discrete teams of cells in additional caudal zones. Neurones that innervate the pharynx lie in the intermediate space, and neurones that innervate the oesophagus and taste bud are rostral. The nucleus ambiguus is linked to corticonuclear tracts bilaterally and to many brain stem centres. At its upper finish, a small retrofacial nucleus intervenes between it and the facial nucleus.
Generic 25mg unisom mastercard
A single synaptic terminal could include one or more neuromodulators in addition to a neurotransmitter, normally (although not always) in separate vesicles. Neuropeptides (see later) are practically all neuromodulators, a minimum of in some of their actions. They are saved within dense granular synaptic vesicles of various sizes and appearances. Embryonic synapses first seem as inconspicuous dense zones flanking synaptic clefts. Immature synapses usually seem after birth, suggesting that they could be labile and are bolstered if transmission is functionally effective or withdrawn if redundant. This is implicit in some theories of reminiscence, which postulate that synapses are modifiable by frequency of use to establish preferential conduction pathways. Evidence from hippocampal neurones means that even brief synaptic activity can enhance the energy and sensitivity of the synapse for some hours or longer (long-term potentiation). During early postnatal life, the traditional developmental increase within the quantity and dimension of synapses and dendritic spines is dependent upon the diploma of neural exercise and is impaired in areas of harm or functional deprivation. Excitatory synaptic boutons are proven (C and G), containing small, spherical, translucent vesicles. Also depicted are a bouton with dense-core, catecholamine-containing vesicles (D); an inhibitory synapse containing small flattened vesicles (F); a reciprocal synaptic construction between two dendritic profiles, inhibitory toward the dendrite (A) and excitatory in the opposite direction (H); an inhibitory synapse containing giant flattened vesicles (I); two serial synapses-one (J) excitatory to the dendrite and one (K) inhibitory to J; and a neurosecretory ending (L) adjoining to a vascular channel (M), surrounded by a fenestrated endothelium. All the boutons in this diagram are of the terminal sort aside from G, which is a bouton de passage. Neurotransmitters 16 Chapter 2 / Overview of the Microstructure of the Nervous System functionally built-in techniques. Many of these are peptides: greater than 50 (together with other candidates) operate primarily as neuromodulators and affect the actions of classic transmitters. Many parasympathetic, and some sympathetic, ganglionic neurones are also cholinergic. Neurones that synthesize the monoamines embody sympathetic ganglia and their homologues, the chromaffin cells of the suprarenal medulla and paraganglia. Noradrenaline is the chief transmitter current in sympathetic ganglionic neurones with endings in various tissues, notably clean muscle and glands, and in other websites, together with adipose and haemopoietic tissues and the corneal epithelium.

Paeonia paradoxa (Peony). Unisom.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- What is Peony?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Peony work?
- Dosing considerations for Peony.
- Muscle cramps, gout, osteoarthritis, breathing problems, cough, skin diseases, hemorrhoids, heart trouble, stomach upset, spasms, nerve problems, migraine headache, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96082
Unisom 25 mg lowest price
Binge consuming (heavy consumption of alcohol for 1�3 days) during pregnancy could be very prone to produce fetal alcohol effects. The susceptible interval of mind growth spans the most important part of gestation; due to this fact, the most secure recommendation is complete abstinence from alcohol during being pregnant. Androgens and Progestogens Androgens and progestogens may affect the female fetus, producing masculinization of the external genitalia. Despite warnings that cigarette smoking is dangerous to the embryo/fetus, greater than 25% of ladies continue to smoke during pregnancy. A population-based case-control examine revealed that conotruncal and atrioventricular septal defects occur extra frequently in infants of moms who smoke during the first trimester of pregnancy. Nicotine constricts the uterine blood vessels, thereby causing a lower in uterine blood circulate and reducing the provision of oxygen and vitamins available to the embryo or fetus from the maternal blood in the intervillous space of the placenta. Note the skinny upper lip, brief palpebral fissures, flat nasal bridge, short nose, and elongated and poorly fashioned philtrum (vertical groove in the median part of the higher lip). Severe maternal alcohol abuse is believed to be the most common environmental cause of psychological deficiency. The interval of biggest sensitivity is 6 to 12 weeks after fertilization, or 8 to 14 weeks after the last regular menstrual period. Second- and third-trimester exposure could result in psychological deficiency, optic nerve atrophy, and microcephaly. Anticonvulsants Epilepsy impacts approximately 1 in 200 pregnant women, and these girls require remedy with an anticonvulsant. Of the anticonvulsant medication available, phenytoin has been definitively recognized as a teratogen. Fetal hydantoin syndrome occurs in 5% to 10% of children born to moms handled with phenytoins or hydantoin anticonvulsants. Valproic acid has been the drug of selection for the administration of various varieties of epilepsy; nevertheless, its use by pregnant women has led to a pattern of birth defects consisting of poorer postnatal cognitive growth and craniofacial, coronary heart, and limb defects.
Syndromes
- Changes in parenting techniques
- Rapid pulse
- You may notice skipped heartbeats, or times when your heartbeat is very fast or irregular.
- Portable, long-term loop recorders -- allow you to start recording if symptoms occur
- The number of red blood cells (RBC count)
- Septic shock
Cheap 25mg unisom fast delivery
The upper part of the diagram reveals the somatic elements of the spinal nerve roots; the lower half exhibits the visceral components: somatic efferent and preganglionic sympathetic fibres (red), somatic and visceral afferent fibres (blue) and postganglionic sympathetic fibres (black). These prolongations, the spinal nerve sheaths (root sheaths), gradually lengthen as the spinal roots turn out to be increasingly oblique. Each individual dorsal and ventral root runs within the subarachnoid space with its personal overlaying of pia mater. Each root pierces the dura separately, taking a sleeve of arachnoid with it, earlier than becoming a member of throughout the dural prolongation just distal to the spinal ganglion. The dural sheaths of the spinal nerves fuse with the epineurium, within or barely beyond the intervertebral foramina. Shortening or obstruction of this sleeve seen on myelography signifies compression of the spinal nerve. At the cervical level, where the nerves are brief and the vertebral movement is best, the dural sheaths are tethered to the periosteum of the adjacent transverse processes. At the outer end of the foramen, the nerve may lie above or below transforaminal ligaments. At lumbar ranges, though L5 is the biggest nerve, its foramen is smaller than these of L1�4, which renders this nerve significantly weak to compression. Somatic efferent fibres that innervate skeletal muscular tissues are axons of, and neurones in the spinal anterior gray column. Visceral components - Visceral components are additionally afferent and efferent and belong to the autonomic nervous system. Preganglionic visceral efferent sympathetic fibres are axons of neurones in the spinal lateral grey column within the thoracic and upper two or three lumbar segments; they be part of the sympathetic trunk along corresponding white rami communicantes and synapse with postganglionic neurones distributed to non-striated muscle or glands. The preganglionic visceral efferent parasympathetic fibres are axons of neurones within the spinal lateral grey column of the second to fourth sacral segments; they leave the ventral rami of corresponding sacral nerves and synapse in pelvic ganglia. The postganglionic axons are distributed mainly to muscle or glands within the partitions of the pelvic viscera.
Effective 25mg unisom
The meningeal coverings of the spinal roots and nerves are described later on this chapter. The epidural space lies between the spinal dura mater and the tissues that line the vertebral canal. Within the vertebral column, it has been instructed that the outer endosteal Epidural Space 118 Chapter eight / Spinal Cord and Nerve Roots. Note the fusiform cervical and lumbar enlargements of the wire and the changing obliquity of the spinal nerve roots as the wire is descended. The cauda equina is undisturbed on the right however has been unfold out on the left to show its particular person components. L1 Posterior funiculus Posterior median septum Lateral funiculus Central canal Posterior column Thoracic nucleus Lateral column Anterior column S1 Anterior funiculus Anterior median fissure. Note the dorsal nerve rootlets in a single linear row, and the ventral rootlets in three or extra rows. It accommodates loosely packed connective tissue, fats, a venous plexus, small arterial branches, lymphatics and nice fibrous bands that join the theca with the liner tissue of the vertebral canal. These bands, the meningovertebral ligaments, are best developed anteriorly and laterally. There can additionally be a midline attachment from the posterior spinal dura to the ligamentum nuchae on the atlanto-occipital and atlanto-axial levels (Dean and Mitchell 2002). The venous plexus consists of longitudinally organized chains of vessels connected by circumdural venous `rings. In the lumbar area, the dura mater is apposed to the partitions of the vertebral canal anteriorly and hooked up by connective tissue in a fashion that permits displacement of the dural sac throughout movement and venous engorgement. Adipose tissue is present posteriorly in recesses between the ligamentum flavum and the dura. The connective tissue extends for a brief distance through the intervertebral foramina along the sheaths of the spinal nerves. Like the principle thecal sac, the foundation sheaths are partially tethered to the partitions of the foramina by nice meningovertebral Trochlear nerve Tentorial notch Median sulcus of fourth ventricle Trigeminal nerve Transverse dural venous sinus Facial and vestibulocochlear nerves Glossopharyngeal, vagus and accent nerves Accessory nerve, spinal root Vertebral artery First cervical (suboccipital) nerve Atlas, posterior arch Hypoglossal nerve Posterior spinal artery Digastric, posterior belly Atlas, transverse course of Spinal accent nerve Second cervical spinal ganglion Vagus nerve Internal jugular vein Sternocleidomastoid Superior cervical sympathetic ganglion Dura mater Third cervical dorsal ramus Denticulate ligament Spinal accessory nerve Vagus nerve (displaced medially) Common carotid artery Vertebral artery. On the left, the foramina transversaria of the atlas and of the third, fourth and fifth cervical vertebrae have been opened to expose the vertebral artery.
Unisom 25 mg fast delivery
A partition coefficient is a distribution ratio describing how the inhaled anesthetic distributes itself between two phases at equilibrium (partial pressures equal in each phases). Tissue:blood partition coefficients decide uptake of anesthetic into tissues and the time needed for equilibration of tissues with the Pa. The time for equilibration may be estimated by calculating a time constant (amount of inhaled anesthetic that can be dissolved in the tissue divided by tissue blood flow) for every tissue. As a results of this preferential transfer of nitrous oxide, the amount or pressure of an air-filled cavity will increase. Passage of nitrous oxide into an air-filled cavity surrounded by a compliant wall (intestinal gasoline, pneumothorax, pulmonary blebs, air bubbles) causes the gasoline space to expand. Conversely, passage of nitrous oxide into an air-filled cavity surrounded by a noncompliant wall (middle ear, cerebral ventricles, supratentorial space) causes an increase in intracavitary pressure. Cardiac output (pulmonary blood flow) influences uptake and therefore Pa by carrying away either roughly anesthetic from the alveoli. As with alveolar air flow, modifications in cardiac output principally affect the rate of enhance of the Pa of a soluble anesthetic. The pharmacokinetics of the elimination of inhaled anesthetics is dependent upon the size of administration and the blood-gas solubility of the inhaled anesthetic. Diffusion hypoxia occurs when inhalation of nitrous oxide is discontinued abruptly, leading to a reversal of partial stress gradients such that nitrous oxide leaves the blood to enter alveoli. The most compelling proof in opposition to the MeyerOverton concept of anesthesia is the truth that effects of inhaled anesthetics on the fluidity of lipid bilayers is implausibly small and may generally be mimicked by temperature changes of 1�C. Furthermore, not all lipid-soluble drugs are anesthetics, and, in fact, some are convulsants. The most definitive evidence that basic anesthetics act by binding directly to proteins and not a lipid bilayer comes from observations of stereoselectivity. Desflurane and sevoflurane present a specific benefit over other presently obtainable potent inhaled anesthetics in that their decrease blood and tissue solubility allow more exact management over the induction of anesthesia and a extra fast recovery when the drug is discontinued. Cerebral metabolic oxygen requirements are decreased in parallel with drug-induced decreases in cerebral activity. Volatile anesthetics cause doserelated decreases in the amplitude and will increase in the latency of the cortical part of median nerve somatosensory evoked potentials, visible evoked potentials, and auditory evoked potentials.
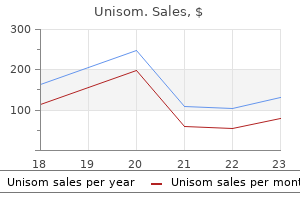
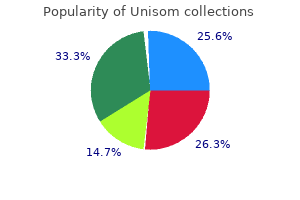
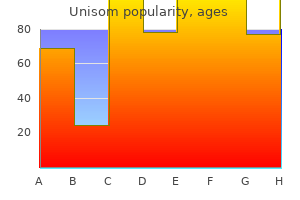
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Unisom
Givess, 38 years: Desflurane produces the highest carbon monoxide concentration (package insert for desflurane describes this risk) followed by enflurane and isoflurane. It passes between the roots of the auriculotemporal nerve and should lie lateral to the tensor veli palatini before entering the cranial cavity by way of the foramen spinosum. This may give rise to a segmental (cross-divisional) sensory loss in syringobulbia.
Marlo, 26 years: Vasopressin is more practical than epinephrine for administration of asystole and the therapy of refractory cardiac arrest. Butyrylcholinesterase (also often identified as plasma cholinesterase or pseudocholinesterase) is synthesized in the liver. Previous treatment with anthracycline antibiotics might improve myocardial depressant results of anesthetic medicine even in patients with normal resting cardiac function.
Mannig, 47 years: Neuronal indicators seem to control the manufacturing of basal laminae by Schwann cells, the induction and upkeep of myelination and, in the mature nerve, Schwann cell survival (few Schwann cells persist in chronically denervated nerves). Forebrain sites, which inhibit spinothalamic tract cells on stimulation, include the periventricular grey matter, ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus and primary sensory and posterior parietal cortices. Subcortical veins drain the deep white matter, deep cortical tissue and subcortical superficial tissue; they terminate, together with cortical veins that drain the cortex, in the meningeal veins.
Seruk, 48 years: The bactericidal motion of penicillins reflects the ability of these antimicrobials to interfere with the synthesis of peptidoglycan, which is an integral part of cell walls of prone micro organism. Fragile vesicles seem on exposed areas of the pores and skin and heal with scarring in patients with porphyria cutanea tarda, a genetic disease that causes cirrhosis and is more frequent in these with hepatitis C. Optic tract fibres terminate primarily in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus, but in addition in the superior colliculus, pretectal space, suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus and inferior pulvinar.
Leon, 59 years: The paired vocal cords connect posteriorly to the vocal course of of each arytenoid and anteriorly meet on the junction of the thyroepiglottic ligament of the anterior portion of the thyroid cartilage. Postoperative liver dysfunction has been associated with most unstable anesthetics, with halothane receiving the most attention. Move: � Passive motion: ask the patient to loosen up and permit you to transfer the joint in its regular anatomical instructions; note restricted extension (called fixed flexion deformity) or limited flexion (called fastened extension deformity).
9 of 10 - Review by L. Irhabar
Votes: 212 votes
Total customer reviews: 212
References
- Tahernia AC, Bricker JY, Ott DA, et al: Intracardiac fibroma in an asymptomatic infant. Clin Cardiol 1990; 13:506-512.
- Sargeant IR, Tobias JS, Blackman G, et al. Radiotherapy enhances laser palliation of malignant dysphagia: a randomised study. Gut 1997;40(3):362-369.
- Vari RC, Boineau FG, Lewy JE: Angiotensin or thromboxane receptor antagonism in rats with congenital hydronephrosis, J Am Soc Nephrol 3(8):1522n 1529, 1993.
- Chua DT, Ma J, Sham JS, et al. Long-term survival after cisplatin-based induction chemotherapy and radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a pooled data analysis of two phase III trials. J Clin Oncol 2005;23(6):1118-1124.
- Theroux MC, Brandom BW, Zagnoev M, et al. Dose response of succinylcholine at the adductor pollicis of children with cerebral palsy during propofol and nitrous oxide anesthesia. Anesth Analg 1994;79:761.
- Althof S, McMahon C, Waldinger M, et al: An update of the International Society of Sexual Medicine?s guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of premature ejaculation (PE), J Sex Med 11(6):1392-1422, 2014.
- Churg A. Fiber counting and analysis in the diagnosis of asbestos-related disease. Hum Pathol 1982;13:381-92.

